Quanto è utile/interessante questa discussione:
| Autore |
Discussione |
|
|
dryice
Nuovo Arrivato

6 Messaggi |
 Inserito il - 22 giugno 2011 : 16:52:48 Inserito il - 22 giugno 2011 : 16:52:48



|
Ciao.
C'è qualcuno che mi può aiutare per l'inserimeto dei valori di espressione "grezzi" nel programma GeNorm per valutare quali hosekeeping utilizzare per analizzare i miei campioni? Per l'analisi dei dati di espressione utilizzo il programma Genex fornito dalla biorad che dà i dati di espressione già normalizzati tramite il metodo delta-delta Ct. Come faccio a d avere i raw data ottenibili con il delta CT metodo, senza utilizzare il reference gene (senza quello Genex non va avanti e mi segnala errore)che sono poi i dati utilizzati da GeNorm?
Grazie,
|
|
|
|
|
GFPina
Moderatore
    

Città: Milano

8408 Messaggi |
 Inserito il - 24 giugno 2011 : 01:03:09 Inserito il - 24 giugno 2011 : 01:03:09




|
| GeNorm ha un chiarissimo manuale di istruzioni, si trova nel sito da cui scarichi GeNorm. Trovi anche i link nel forum nelle altre discussioni in cui si parla di GeNorm. |
 |
|
|
dryice
Nuovo Arrivato

6 Messaggi |
 Inserito il - 24 giugno 2011 : 08:46:34 Inserito il - 24 giugno 2011 : 08:46:34




|
Citazione:
Messaggio inserito da GFPina
GeNorm ha un chiarissimo manuale di istruzioni, si trova nel sito da cui scarichi GeNorm. Trovi anche i link nel forum nelle altre discussioni in cui si parla di GeNorm.
 L'ho letto. Non c'è scritto però come convertire i valori di Ct in quantità relative (RQ) che sono poi i dati grezzi (raw data) richiesti dal programma per effetture la scelta dei geni reference. Temo ci voglia un altro software (tipo qbasePLUS) che io non ho. L'ho letto. Non c'è scritto però come convertire i valori di Ct in quantità relative (RQ) che sono poi i dati grezzi (raw data) richiesti dal programma per effetture la scelta dei geni reference. Temo ci voglia un altro software (tipo qbasePLUS) che io non ho. |
 |
|
|
GFPina
Moderatore
    

Città: Milano

8408 Messaggi |
 Inserito il - 24 giugno 2011 : 13:26:34 Inserito il - 24 giugno 2011 : 13:26:34




|
Citazione:
Messaggio inserito da dryice
 L'ho letto. Non c'è scritto però come convertire i valori di Ct in quantità relative (RQ) che sono poi i dati grezzi (raw data) richiesti dal programma per effetture la scelta dei geni reference. L'ho letto. Non c'è scritto però come convertire i valori di Ct in quantità relative (RQ) che sono poi i dati grezzi (raw data) richiesti dal programma per effetture la scelta dei geni reference.
C'è scritto, c'è scritto!
Questo è il manuale: http://medgen.ugent.be/~jvdesomp/genorm/geNorm_manual.pdf
pag. 6 "5. Normalization flow chart"
ti spiega proprio come si fa:
Citazione:
The Ct values are transformed to quantities (either by using standard curves or the comparative Ct method). Here, the highest relative quantities for each gene are set to 1. These raw -not yet normalized- reference gene quantities are the required data input for geNorm.
ci sono anche i conti (te li riscrivo anche io sotto)
pag. 9 "7. Requirements"
Citazione:
4. The input file should be an Excel data table, with the first column containing the sample names and the first row containing the gene names. The first cell of the first row and column (cell A1) should be empty. The other cells contain the relative gene expression levels. Empty cells are NOT allowed. The input file should be saved in the InputData directory, where also an example data file is located.
Raw expression levels are needed for input; these are the quantities (NOT Ct values!) obtained from a real-time RT-PCR run, either trough a standard curve, or via the delta-Ct method (also called comparative Ct method, see FAQ section for more information).
Infine a pag. 12
Citazione:
Q8: What is the difference between the delta-delta-Ct and delta-Ct method?
A9: The delta-delta-Ct method transforms Ct values into normalized relative expression levels, by relating the Ct value of your target gene in your sample to a calibrator/control sample AND to the Ct value of a reference gene in both samples. Note that in the original publication of the deltadelta-Ct method (Applied Biosystems technical bulletin), there’s no correction for a difference in amplification efficiency between the target and reference gene (only the underlying requirement that the efficiency of target and reference gene should be similar).
In the delta-Ct method, you don't use any reference gene; you just relate the Ct value of your gene (either target or reference) to a control/calibrator. This control/calibrator can be any sample: e.g. a real untreated control, or the sample with the highest expression (lowest Ct value). The delta-Ct method generates raw (not-normalized) expression values, which need to be normalized by dividing with a proper normalization factor.
Doing 3 times delta-delta-Ct between your gene of interest and 3 reference genes, and then taking the geometric mean of the 3 relative quantifications, is the same as first transforming the Ct values of your 4 genes to quantities using delta-Ct, and dividing the gene of interest by the geometric mean of the reference genes. Although both approaches yield the same result, I favour the delta-Ct method, because a) it's much easier to do in Excel, b) it's very easy to take different amplification efficiencies for the different genes into account (just replace value 2 with the actual efficiency of the gene (e.g. 1.95 for 95%) in the formula of delta-Ct), and c) it allows easy inclusion of multiple reference genes for normalization.
Quindi devi semplicemente utilizzare il delta Ct.
A pag. 6 come ti dicevo trovi una tabella, io ho ripreso i dati del primo HK e ho riscritto i conti:
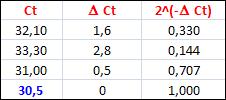
Tu hai i tuoi Ct
- prendi il Ct più basso "Ct min." (quello che ho segnato in blu)
- calcoli il deltaCt (= Ct - Ct min.)
- calcoli 2^(-deltaCt)
ottieni i "raw data" da utilizare in GeNorm! |
 |
|
|
dryice
Nuovo Arrivato

6 Messaggi |
 Inserito il - 24 giugno 2011 : 13:42:18 Inserito il - 24 giugno 2011 : 13:42:18




|
grazie mille. Confesso, non avevo visto la formula.
A buon rendere |
 |
|
| |
Discussione |
|
|
|
Quanto è utile/interessante questa discussione:
| MolecularLab.it |
© 2003-18 MolecularLab.it |
 |
|
|




 L'ho letto. Non c'è scritto però come convertire i valori di Ct in quantità relative (RQ) che sono poi i dati grezzi (raw data) richiesti dal programma per effetture la scelta dei geni reference. Temo ci voglia un altro software (tipo qbasePLUS) che io non ho.
L'ho letto. Non c'è scritto però come convertire i valori di Ct in quantità relative (RQ) che sono poi i dati grezzi (raw data) richiesti dal programma per effetture la scelta dei geni reference. Temo ci voglia un altro software (tipo qbasePLUS) che io non ho.